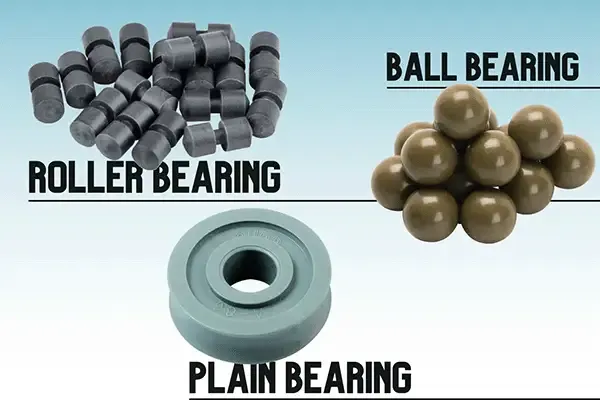
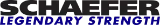The three most common types of bearings found in a sailing block / pulley are plain bearings, ball bearings and roller bearings.
The three most common types of bearings found in a sailing block / pulley are plain bearings, ball bearings and roller bearings.
But, what’s the difference between the three and why should you choose one over the other? Making the correct choice can help your rope system run more efficiently and to the desired performance.
But first, what is a bearing?
A bearing essentially assists in the rotation of an object and is used in many different applications to help reduce friction and wear. Bearings can be used in many different items including bikes, cars, air conditioning units, washing machines, and many other everyday objects. In all of these products, a bearing allows two parts to move separately from each other whilst still remaining in contact.
Bearings in sailing pulleys have two major functions, to reduce friction and save energy.
If you rub two materials together you get friction. Friction causes wear over time as well as creates a loss of energy.
Imagine trying to move a large heavy box along the ground just by pushing it. The friction between the ground and the box makes it really hard for you to push. Now imagine putting that same box on top of a skateboard and trying the same thing. The skateboard has wheels and the wheels would in this instant act as bearings. It would take you much less energy to push the box on top of the skateboard as there is now less surface touching the ground.
 Plain Bearing Blocks
Plain Bearing Blocks
A plain bearing block is simply a sheave mounted directly onto an axle, which it then rotates around. You can see all the component parts of our A2030P in the explosion line drawing.
Plain bearing blocks typically have quite a high breaking load as the sheave and the axle share the load from the rope evenly. You won’t find a maximum working load (MWL) for our plain bearing blocks, as the MWL is the load at which the bearing system can get damaged and will no longer perform as designed. As there are no ball or roller bearings to damage a plain bearing block will perform the same across the whole breaking load range until a major component gives way.
However, without the use of ball or roller bearings, the contact surface between the sheave and axle is much greater and thus results in more friction when the sheave rotates. This results in more energy being used to spin the sheave.
Our plain bearing blocks feature a grey sheave, to differentiate them from the dynamic bearing range which has a black sheave. So you can quickly and easily identify which type of block you have.
Plain bearing blocks have a limited number of parts making them much easier to manufacture and assemble. This usually results in a more budget friendly block.
In summary, a plain bearing block is great for:
Applications that feature a high static load.
Applications that do not require quick or constant adjustment.
Offering a more budget friendly option.
 Ball Bearing Blocks (Dynamic Blocks)
Ball Bearing Blocks (Dynamic Blocks)
As the name suggests, ball bearing blocks (or dynamic blocks as we call them) feature balls to separate the sheave from the central axle.
A ball bearing is the most efficient shaped bearing for fast rolling speeds. The contact between the sheave, bearing and axle is minimal which results in the lowest possible friction. This allows the sheave to spin much faster with less energy, when compared to plain and roller bearings.
However, this minimal contact between the sheave, balls and axle generates point loading. This is why it’s not recommended to regularly exceed the suggested MWL of a dynamic block, as it can cause deformation or damage to the three components.
So, ball bearing blocks can spin extremely quickly, with very little energy. But cannot withstand the same high loads when compared to plain or roller bearings.
In summary, Ball bearing blocks are great for:
Fast running systems.
Maximum friction reduction.
Lower loaded and regularly adjusted lines.
 Roller Bearings (High Roller Blocks)
Roller Bearings (High Roller Blocks)
Roller bearings are also commonly known as needle bearings and as the name suggests, they are cylindrically shaped.
Roller bearings are a great alternative to a ball bearing or plain bearing block as they offer “best of both” performance.
Due to the larger surface/ contact area, roller bearings will not roll as quickly as ball bearings. However, they are much more efficient than a plain bearing system.
Thanks to the larger surface area the roller bearing can withstand higher working loads without compromising strength and shape when compared to the ball bearing, as the load between the three components can be more evenly shared. The result is a bearing system that can roll fairly efficiently and at higher loads than a ball bearing would be able to. However, the surface area results in a bigger energy loss to create a similar rolling speed.
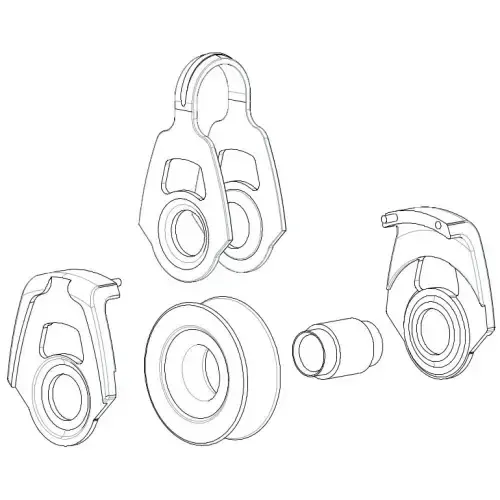
The exploded line drawing shows all the component parts of our A9060 high roller block. As you can see, this block features both ball bearings and roller bearings. This is common in roller blocks. The roller bearings take the load of the sheave when in use and the ball bearings offer a secondary side load support. The ball bearings stop the sheave from being able to “wobble” side to side but do not take any of the actual load put on the block when in use.
These features make roller bearing blocks a great choice for highly loaded applications that require smooth regular adjustment.
 In summary, a roller bearing block is great for:
In summary, a roller bearing block is great for:
Highly loaded applications.
Lines that take a high static load, but still require regular adjustment.
Lines that need to run quickly.
Other things to consider.
By now, you hopefully have a basic understanding of the difference between the three styles of bearings. If you want to get even more technical, there are a couple of additional things you can consider.
Bearing materials.
Caged vs non-caged bearings.
The above information will be available soon. So check back here for further details on bearings in the future.